N-Tier Architecture
Short introduction to Multi-Tier Architecture
Common layers
Presentation layer
Application layer
Database layer
Common Architectures
Single Tier architecture
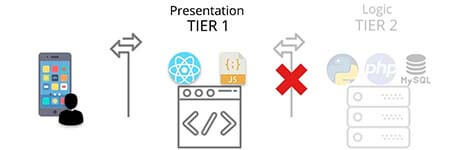
Two Tier architecture
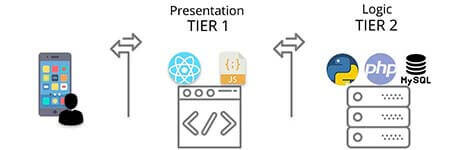
Links & Resources
Last updated